
Next, lets start configuring the capture. This ACL will get specific traffic for the remote destination of 1.1.1.1. To monitor traffic to a specific site we might do something like this: ip access-list extended CAPTURE_ACL Build an access list to account for traffic flowing in both directions if you do in fact want to see both sides of the flow. Ideally, you may want to leverage an extended access list. Second, you want to come up with some way of filtering traffic. Let’s look firsthand at how to configure and use the capture features of the switch.įirst, take note that this configuration takes place in enabled mode, not configuration mode.
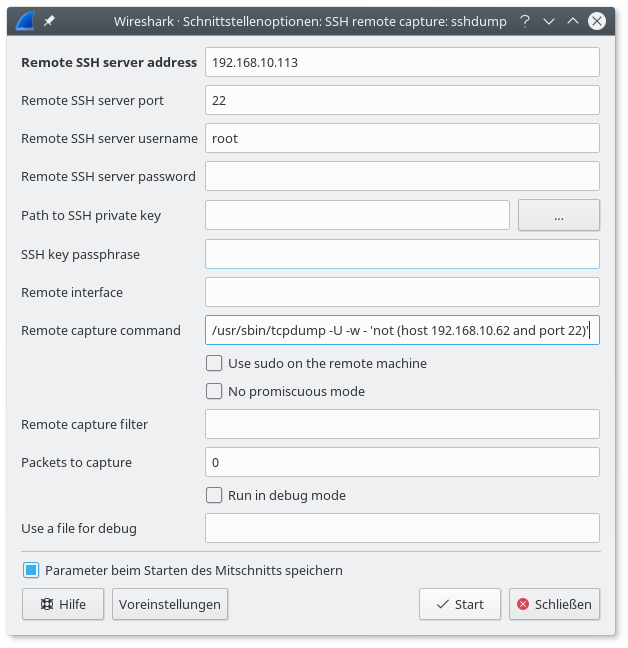
With this comes some additional flexibility, in this case, Wireshark. In the case of Cisco 36 switches the management and control planes are essentially a Linux operating system with a terminal to function like IOS of the past.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001_wireshark-tutorial-4143298-52d1294a66f64810b14dbfc6fdbe00de.jpg)
With today’s less expensive and more powerful hardware it should come as no surprise that this functionality is now available on network hardware it’s self. I’ve written about this in the past here. Historically the easiest way to do this was to configure some type of SPAN port on a switch to copy the traffic to your pack capture device.

One of the most fundamental troubleshooting concepts in all of IT is to capture packets and review the data as it flows over the wire.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
